Prenatal tests – what can you expect?

To all the parents-to-be, congratulations on your bundle of joy! These upcoming months are going to be an amazing journey for you and your other half. We know that all parents want to be as ready as possible for their baby, so here's a quick rundown of the different prenatal tests you can expect and talk about with your OBGYN doctor.
What are prenatal tests?
Prenatal tests are medical tests you get during pregnancy. These are tests to check the mother’s and her baby’s health. With the help of modern science, you can find out if a baby is at risk for problems like preterm birth, chromosomal abnormalities, and foetal abnormalities.
Basically, there are two types of prenatal tests:
- Screening tests
These tests are a gauge to identify whether a condition is present in your baby. It does not give a definite answer, and is often used as an indicator. A few examples of prenatal screening tests are blood tests and specific types of ultrasound. - Diagnostic tests
Prenatal diagnostic testing will give you an accurate diagnosis to whether your little one might carry certain health conditions. However, these are invasive and are only recommended when a screening test shows indication of a disorder.
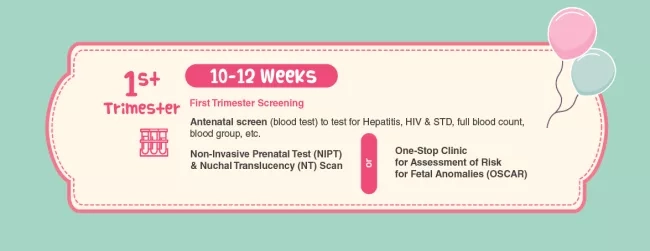
1st Trimester
In your first trimester, you should focus on antenatal screening tests. It helps to screen for chromosomal abnormalities, hepatitis, sexual transmitted diseases and many more. These screening tests are non-invasive and will not cause any miscarriage risk to the pregnancy.
Also, because women are having babies later in life, prenatal screening tests are more important than ever.1 As maternal age rises, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities increases as well. Early detection for your little one is important, and many mommies-to-be are encouraged to take these tests to get a better understanding of the future.
There are two available options for testing chromosomal abnormalities:
Remember to consult your OBGYN doctor and do your research before taking any of these tests.
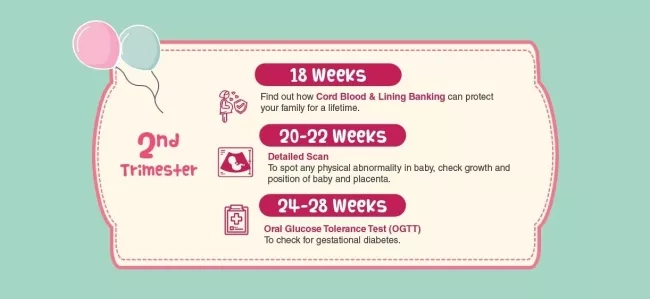
2nd Trimester
In the course of your second trimester, your baby’s organs have become more developed, and towards the end of your second trimester, your baby starts to get active. Mommies-to-be will begin to feel the joy of your little one moving around and kicking.
During this period, an important service to consider is cord blood and cord lining banking. Get educated on how stem cells play a part in being biological insurance for your family and how the collection process by your OBGYN doctor is painless, simple, and risk-free. As the umbilical cord stem cells can only be collected at birth, do take some time to understand this more.
Week 20 to 28 of your pregnancy is when you should go for your detailed scanning and oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT).
- Detailed scanning
A second trimester detailed scan is an ultrasound scan which allows the doctor to check your baby’s body structure. It’s used to spot any physical abnormalities, check growth, the position of your baby and the placenta. Ultimately, this scan helps to prepare you and your doctor for the delivery and care of your little one after birth. - Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
An OGTT is simply a test that measures how well your body responds to glucose after you consume a specific amount of sugar. Firstly, you will have to fast overnight. On the day of your OGTT, a blood sample will be taken from you on an empty-stomach. This will determine your glucose level when you are fasting. You will then need to drink a glucose solution given by the nurse. Your blood samples will be taken after 1 and 2 hours after you consuming the solution. This test ultimately diagnose whether you might have gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
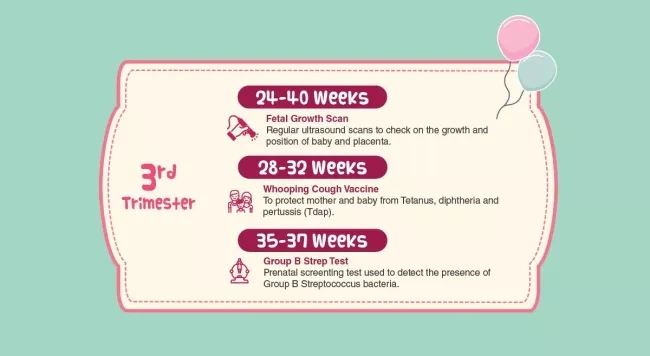
3rd Trimester
In your third trimester, it is soon to be a home run for you! We understand that you may feel even more uncomfortable due to the weight gained, sleepless nights and might go through labour contractions that are false (also known as Braxton-Hicks). Our piece of encouragement is to hang in there, mommies-to-be. You will see your little one very soon, and good job so far.
The tests that will be required are the whooping cough vaccine and group B strep.
- Whooping cough vaccine
It’s strongly encouraged by many for pregnant mothers to undergo the whooping cough vaccine. The purpose of this vaccine is to prevent you and your baby from contracting tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (Tdap). These illnesses are highly contagious and therefore it’s important to get vaccinated to protect your baby. - Group B strep test
What is Group B streptococcus you may ask? It is a type of bacteria that is found in the vagina or the rectum in 30% to 40% of women.2 The concern rises when the bacteria has been passed on to your little one through normal delivery. The infection usually manifests in a form of pneumonia or meningitis in your child.
This information may seem very serious. Fret not, there is a test to see if mommies are carriers of this bacteria. If they happen to be tested positive, they can be treated with doses of antibiotics to reduce the chances of passing it to your baby.
To all the parents-to-be, these are just nuggets of information to better prepare you for your pregnancy journey. Always remember to consult your OBGYN doctor to understand what other details you might need before performing any tests.
References:
1Strategy Group Singapore. (2011). Marriage and Parenthood Trends in Singapore. https://www.strategygroup.gov.sg/images/Press%20Release%20images/PDFs/marriage-and-parenthood-trends-in-singapore.pdf
2Vaginal Discharge During Pregnancy. (2019, August 9). Retrieved July 29, 2020, from https://www.healthhub.sg/live-healthy/993/pregnancy-vaginal-discharge-during-pregnancy
Recent Blog Posts
- 01 Aug 2025
- 02 Jun 2025
- 28 Mar 2025
- 10 Nov 2023
- 19 Oct 2022
